雄州城市规划
中国,江苏,南京(2014)
用地面积:17,300公顷
项目类型:城市设计,总体规划,区域规划
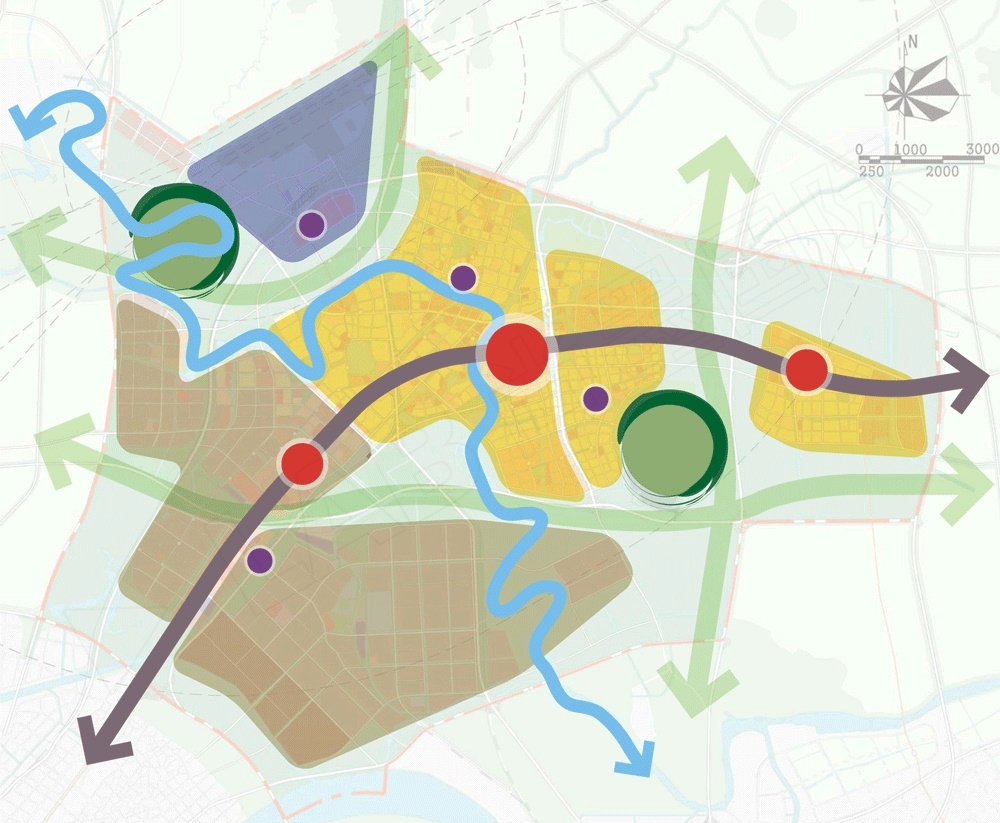
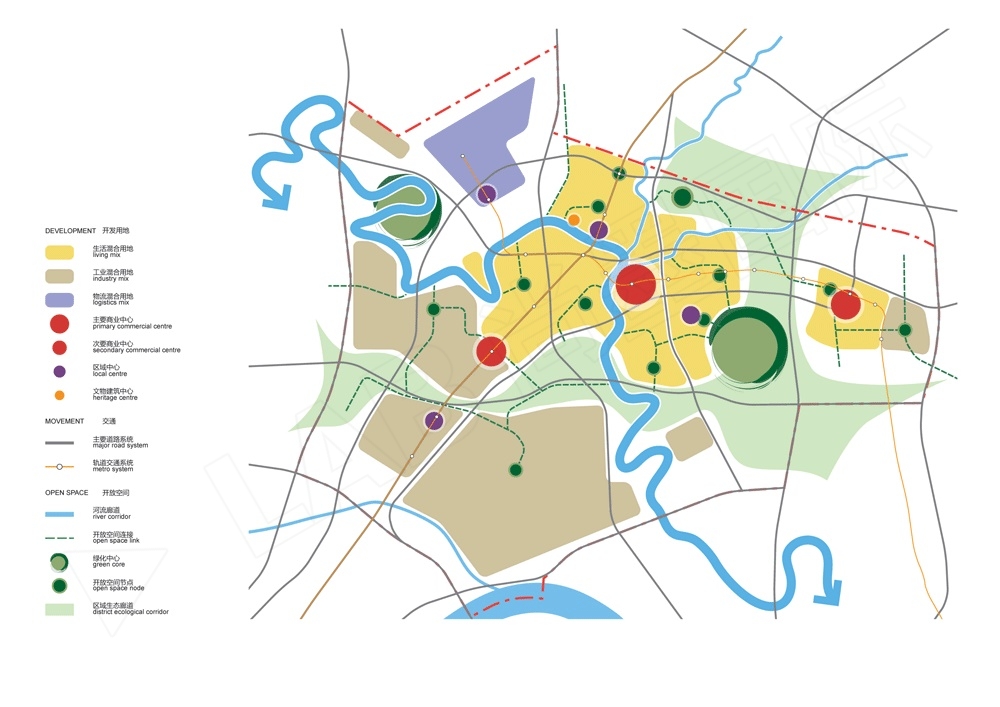
本次规划的规划结构平面展现了一个更为合理的开发区域划分。每个区域都给予主要道路系统的交叉口或中央轴线设置。主要的商业中心是基于地铁系统设置,区域中心及开放空间节点由开放空间网络连接起来。规划沿着滁河生态带布置有两个中心——河岸湿地公园以及灵岩山。发展轴线从西南角的龙池中心向东北角的衡量中心呈弧线展开。一个新的雄州中心位于轴线的中央,紧邻滁河。六大开发组团,每一个都具备区域中心,并且位于主要生态走廊之间。
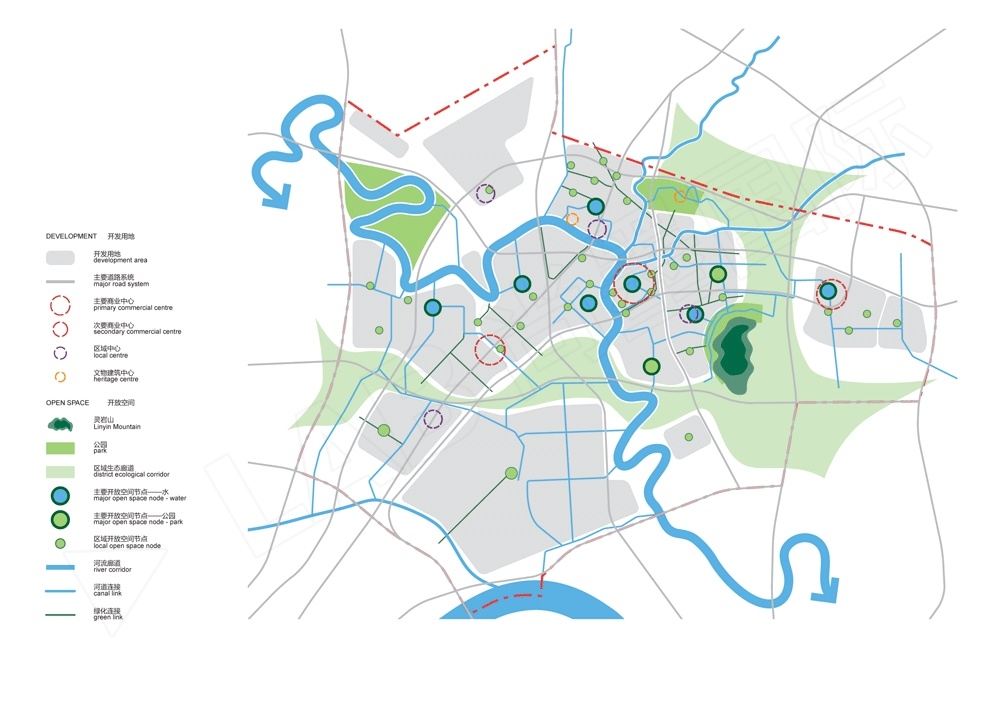
开放空间规划平面图显示了更为详细的开放空间节点类型及其连接。三个主要的公共绿地围绕着雄州片区建立:西侧的滁河湿地,北侧的棠邑遗址公园,东侧的灵岩山公园。
开放空间节点主要分为2个类型:以水景为中心,以花园为中心。他们在沿着绿色及运河开放空间廊道与一些小型的区域绿色空间衔接。
The structure plan shows a reasonable division of the development precincts, each based around an intersection or central spine of the major road network. Major commercial centres are based on the metro system, while local centres and open space nodes are connected by the open space network.
The full open space plan shows a greater detail of open space node types and their connectivity. Three main public parklands are established around Xiongzhou: the river wetlands in the west; Tang Yi historic park in the north; and Lingyin Mountain park in the east.
Key open space nodes are of two types – those with water features as the centre; and those with garden centres. Along with the smaller local green spaces they are generally connected along open space corridors of canals and green links.